Minjung Kim (Master Graduate Student)
 |
Graduate Student, Embedded System Architect |
Repository Commit History
 |
Introduction
Full Bio Sketch
Mr. Kim is about to graduate from electronic engineering in Kyungpook National University. He is currently B.S student at ai-soc laboratory. His research interests include overcoming the limits of Embedded System. His recent study is about deadline scheduling algorithm and memory saving technique using struct bit field. Also, he conducts research about implementing hypervisor in MCU, by jumping to function pointer. His future work will be about safety techniques of ARM processors such as Failsafe and Trustzone. And also memory saving techniques using Scratchpad is also his interests. His final goal is to implement safe hypervisor in Embedded MCU.
Research Topic
Shallow OS: Deadline Scheduling & struct bit field
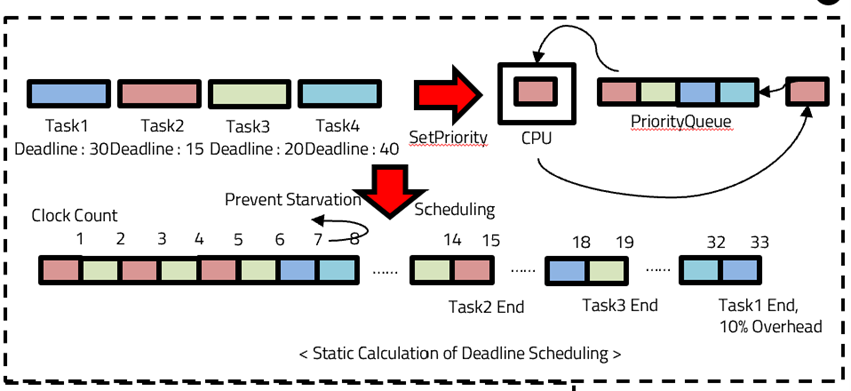 In an Embedded environment, code modification is not possible at runtime, and the available resources are limited due to its small size. In this paper, we propose some methods to overcome these limitations. One is deadline scheduling. Through deadline scheduling, we can predict when the task will finish. For concerns about starvation, we made a new variable and handle the task to not starve. Other advantage is that we can finish high-priority task faster. Another proposal is the struct bit field. By implementing a bit field, we can use resources more efficiently. We also considered overhead by adding a bit field, which contains additional bitwise operation. We achieved a 50% reduction in memory usage without much difference in execution time.
In an Embedded environment, code modification is not possible at runtime, and the available resources are limited due to its small size. In this paper, we propose some methods to overcome these limitations. One is deadline scheduling. Through deadline scheduling, we can predict when the task will finish. For concerns about starvation, we made a new variable and handle the task to not starve. Other advantage is that we can finish high-priority task faster. Another proposal is the struct bit field. By implementing a bit field, we can use resources more efficiently. We also considered overhead by adding a bit field, which contains additional bitwise operation. We achieved a 50% reduction in memory usage without much difference in execution time.
Multi OS on Lightweighted MCUs
 Unlike the way that only single applications were uploaded to the existing MCU, I downloaded two discrete projects named OS1 and OS2, which I made to act as OS. Each OS has discrete memory sections in both SRAM and flash, which ensure safety. Work for context switching takes place immediately before and after jumping to the Monitoring app. In the function for context switching, not only context save and restore, but also I/O device virtualization occurs. By using I/O virtualization, each OS will be able to feel as if it is exclusively using an I/O device during execution time.
Unlike the way that only single applications were uploaded to the existing MCU, I downloaded two discrete projects named OS1 and OS2, which I made to act as OS. Each OS has discrete memory sections in both SRAM and flash, which ensure safety. Work for context switching takes place immediately before and after jumping to the Monitoring app. In the function for context switching, not only context save and restore, but also I/O device virtualization occurs. By using I/O virtualization, each OS will be able to feel as if it is exclusively using an I/O device during execution time.
Dynamic Round-Robin Scheduling on Bare-Metal Shallow Multi-OS
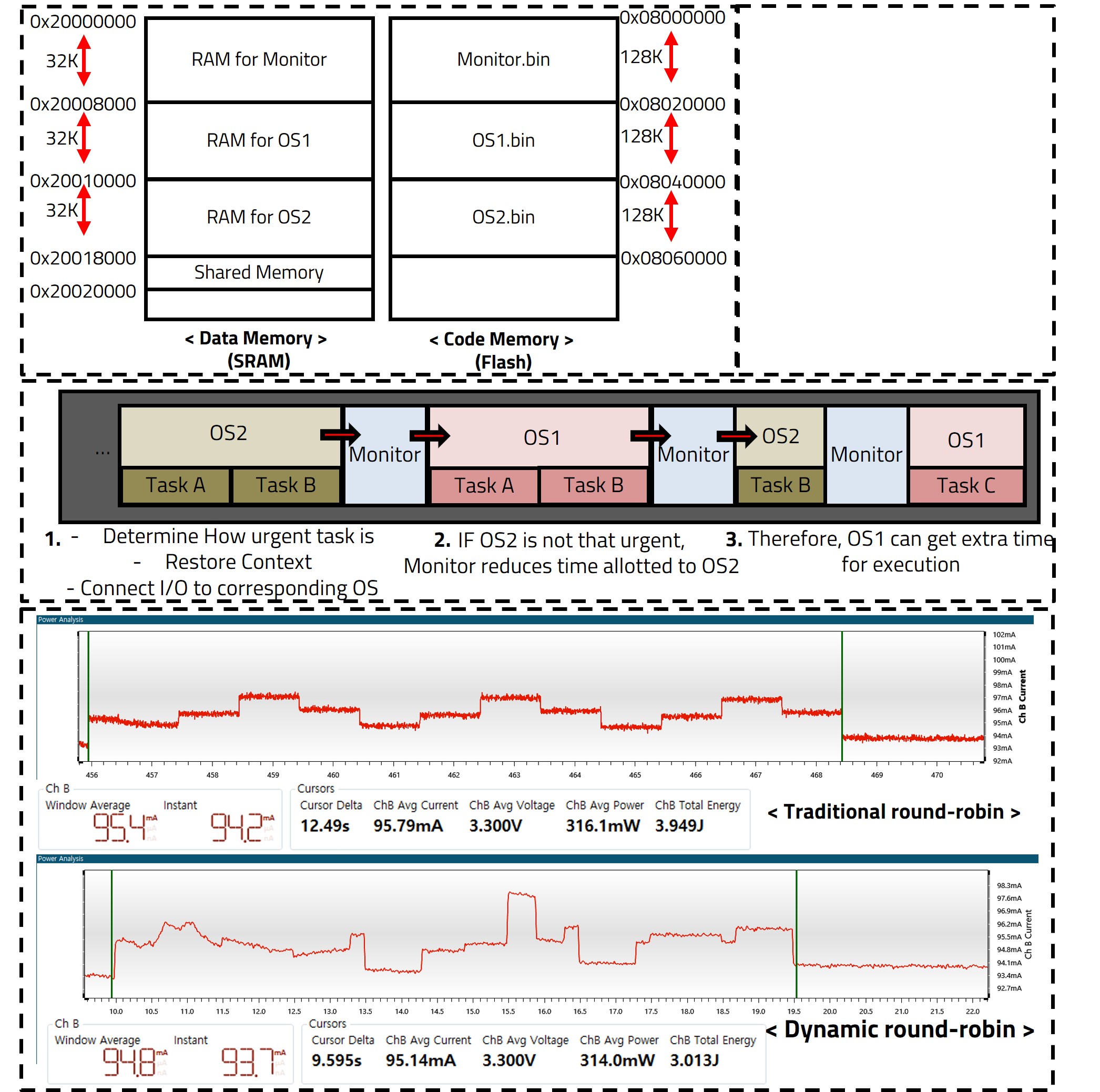 In recent years, there has been a tendency to integrate functions using a small number of microcontrollers instead of using multiple microcontrollers in various environments. In order to support this flow, the need for a hypervisor that can use resources light and efficiently has emerged. In this paper, we propose hypervisor using dynamic round robin that can fluidly adjust the time quantum according to the urgent of each OS. In addition, a monitor mode was created to manage resources between each OS, and an ultra-light context switch was added to the monitor mode to increase responsiveness while managing multiple OS. When using the system proposed in this paper, the execution time of the test code decreased by about 36 percent compared to the traditional round-robin. Moreover, in terms of power, an average gain of about 3mA was achieved, and it was found that the ultra-light context switch uses only about 5 percent of the cycle compared to FreeRTOS.
In recent years, there has been a tendency to integrate functions using a small number of microcontrollers instead of using multiple microcontrollers in various environments. In order to support this flow, the need for a hypervisor that can use resources light and efficiently has emerged. In this paper, we propose hypervisor using dynamic round robin that can fluidly adjust the time quantum according to the urgent of each OS. In addition, a monitor mode was created to manage resources between each OS, and an ultra-light context switch was added to the monitor mode to increase responsiveness while managing multiple OS. When using the system proposed in this paper, the execution time of the test code decreased by about 36 percent compared to the traditional round-robin. Moreover, in terms of power, an average gain of about 3mA was achieved, and it was found that the ultra-light context switch uses only about 5 percent of the cycle compared to FreeRTOS.
Compress data and partial execution
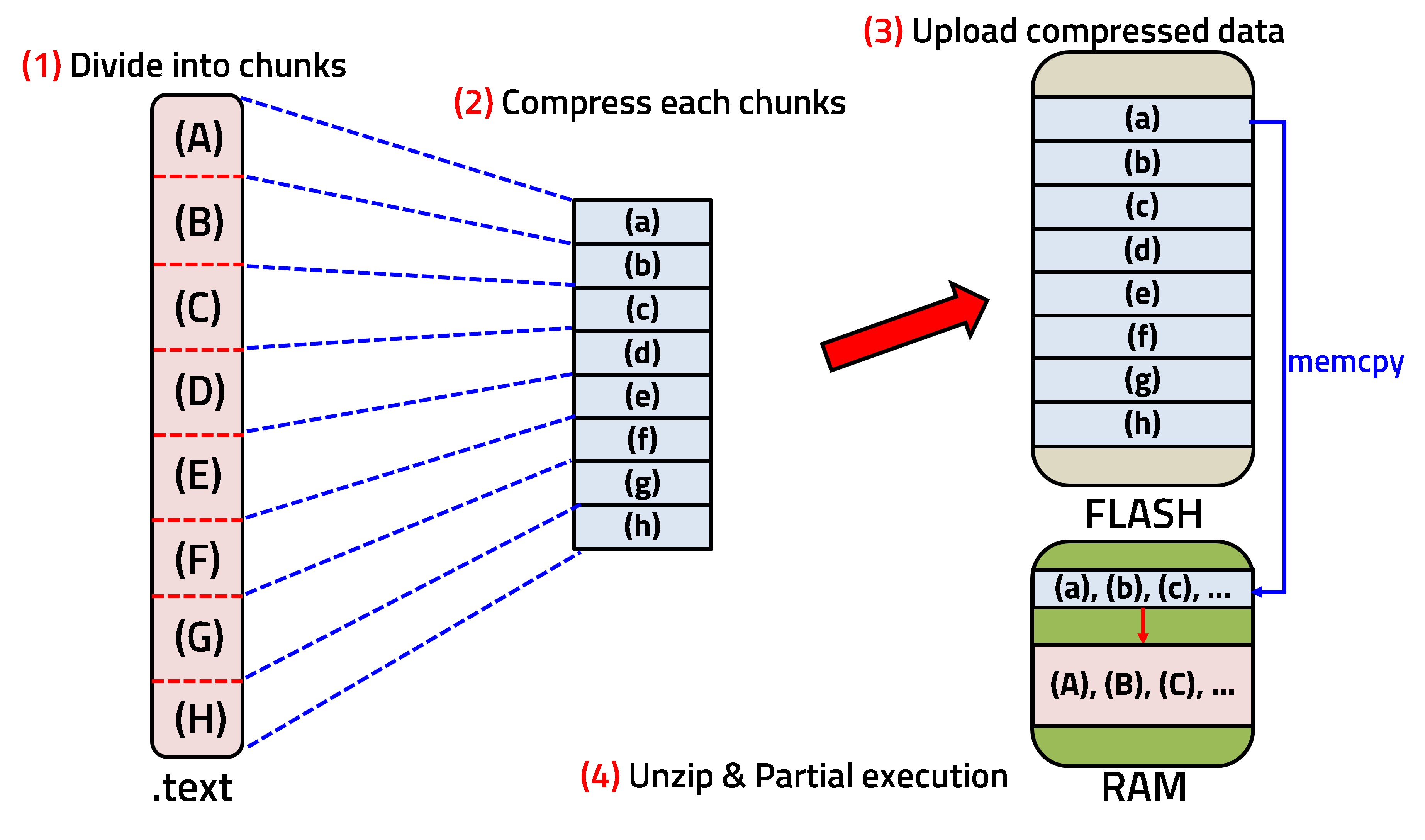 In an embedded environment, runtime code modification is not possible, and available resources are limited due to its small size. In this paper, we propose a code expansion technique using compression to overcome these limitations. This method is designed to execute a program that is larger than the physical Flash memory capacity.
The program is stored in Flash in a compressed format, then decompressed into RAM for execution at runtime.We specifically address the potential for high memory overhead during the decompression phase, which is a critical concern in RAM-constrained environments.
To mitigate this, our method involves partitioning the executable code from the final linked ELF file into fixed-size chunks and compressing each chunk independently. On the target device, these chunks are decompressed incrementally, one by one, into a final execution buffer. This approach significantly reduces the peak RAM usage during the restoration process compared to decompressing the entire function at once.As a result, we demonstrated that a function larger than the available Flash memory can be successfully restored and executed in RAM, using only a small, fixed-size temporary buffer for the decompression process. This technique can contribute to implementing dynamic feature expansion in embedded systems with limited memory.
In an embedded environment, runtime code modification is not possible, and available resources are limited due to its small size. In this paper, we propose a code expansion technique using compression to overcome these limitations. This method is designed to execute a program that is larger than the physical Flash memory capacity.
The program is stored in Flash in a compressed format, then decompressed into RAM for execution at runtime.We specifically address the potential for high memory overhead during the decompression phase, which is a critical concern in RAM-constrained environments.
To mitigate this, our method involves partitioning the executable code from the final linked ELF file into fixed-size chunks and compressing each chunk independently. On the target device, these chunks are decompressed incrementally, one by one, into a final execution buffer. This approach significantly reduces the peak RAM usage during the restoration process compared to decompressing the entire function at once.As a result, we demonstrated that a function larger than the available Flash memory can be successfully restored and executed in RAM, using only a small, fixed-size temporary buffer for the decompression process. This technique can contribute to implementing dynamic feature expansion in embedded systems with limited memory.
Runtime Firmware update using multi-flash bank
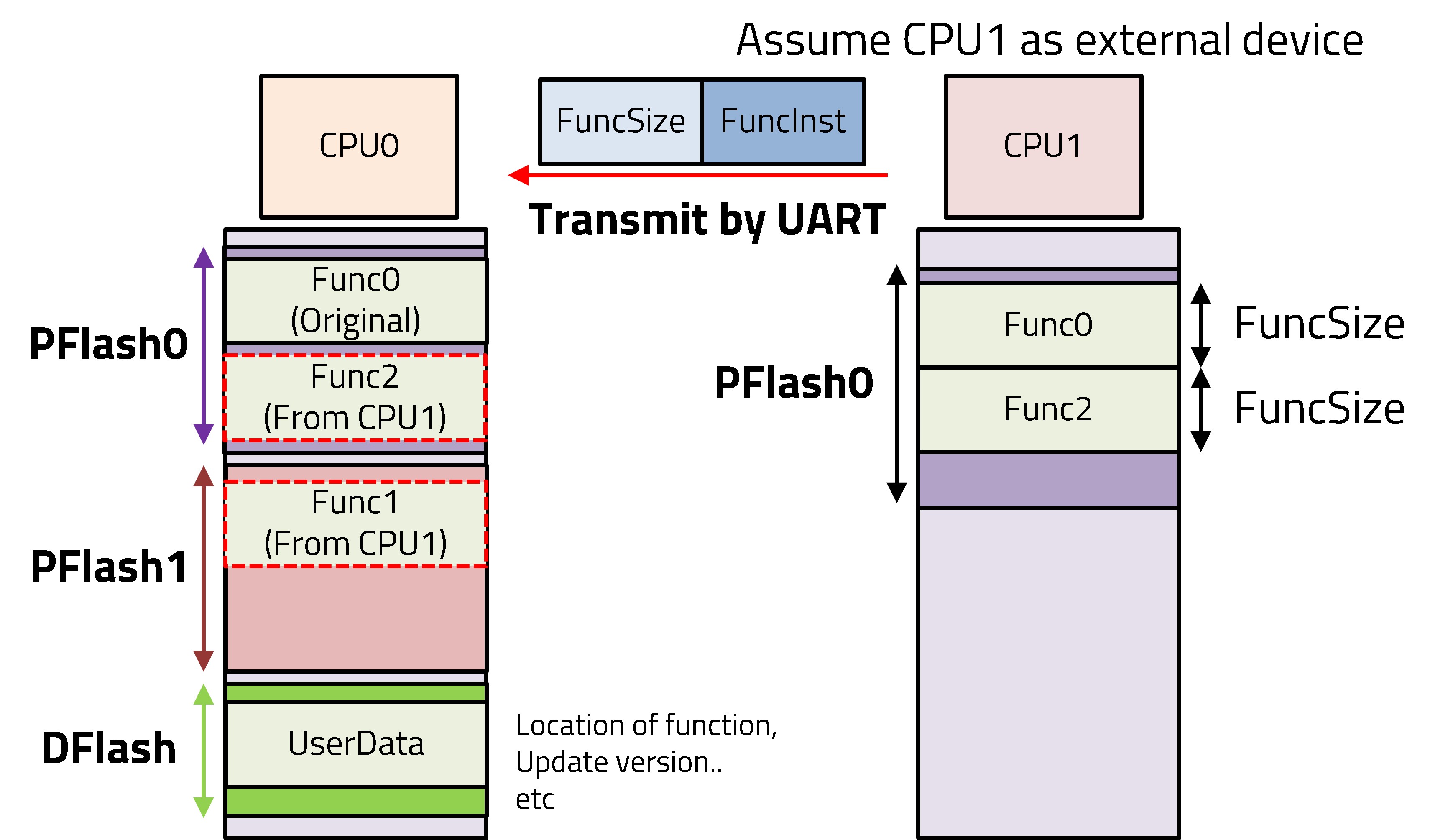 This work introduces a technique for achieving zero-downtime, runtime Over-the-Air (OTA) updates on microcontrollers by utilizing a dual-bank flash architecture. To overcome the service interruptions caused by traditional update-and-reboot cycles, our method allows new code to be integrated while the system is fully operational. We achieve this by executing the main program from one flash bank while simultaneously receiving and writing a new function to a separate, inactive bank. Upon successful download, a function pointer is atomically redirected to the new routine, enabling its immediate execution without a system halt. This approach facilitates the seamless, on-the-fly deployment of feature upgrades and critical patches, making it ideal for high-availability embedded systems in fields such as IoT and industrial control.
This work introduces a technique for achieving zero-downtime, runtime Over-the-Air (OTA) updates on microcontrollers by utilizing a dual-bank flash architecture. To overcome the service interruptions caused by traditional update-and-reboot cycles, our method allows new code to be integrated while the system is fully operational. We achieve this by executing the main program from one flash bank while simultaneously receiving and writing a new function to a separate, inactive bank. Upon successful download, a function pointer is atomically redirected to the new routine, enabling its immediate execution without a system halt. This approach facilitates the seamless, on-the-fly deployment of feature upgrades and critical patches, making it ideal for high-availability embedded systems in fields such as IoT and industrial control.
Symmetric Multiprocessing RTOS in Multi-Core MCU
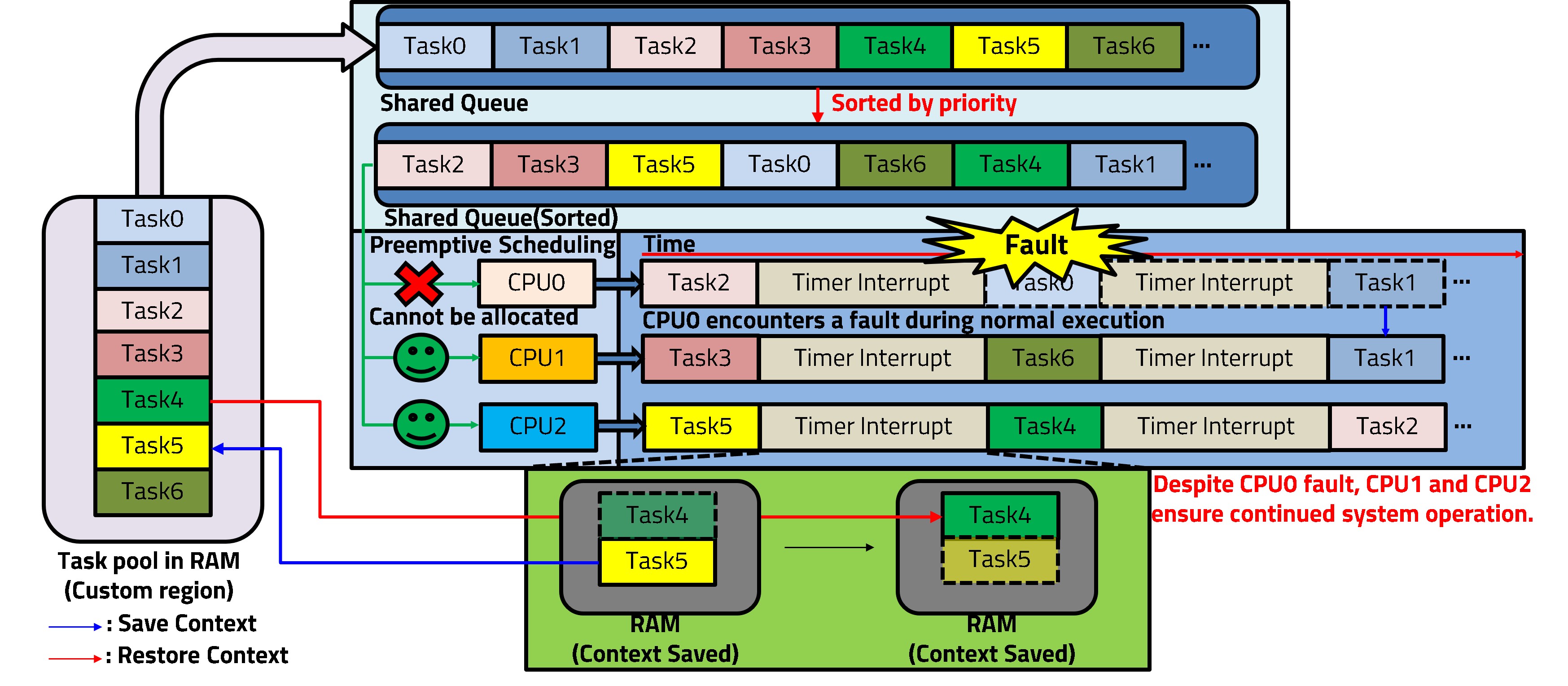 In modern automotive systems, the prevalent Asymmetric Multiprocessing (AMP) model struggles to meet reliability demands. Its static task allocation leads to poor load balancing, vulnerability to core faults, and inefficient interrupt handling. This work introduces a fault-tolerant Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) RTOS to address these limitations. Our system ensures resilience via dynamic task allocation from a shared pool and uses a location-independent mechanism that defers interrupt processing to schedulable tasks, preventing omissions in high-frequency scenarios. Evaluations confirm the method’s superiority: our SMP approach improved system lifespan by 25% through efficient load-balancing and maintained a 92% task completion rate despite core failures. It also handled high-frequency interrupts (below 1 kHz) with 100% completion and service latencies under 100 ms. Ultimately, our proposed RTOS significantly enhances robustness and reliability, making it a highly suitable solution for demanding automotive applications where system integrity is critical.
In modern automotive systems, the prevalent Asymmetric Multiprocessing (AMP) model struggles to meet reliability demands. Its static task allocation leads to poor load balancing, vulnerability to core faults, and inefficient interrupt handling. This work introduces a fault-tolerant Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) RTOS to address these limitations. Our system ensures resilience via dynamic task allocation from a shared pool and uses a location-independent mechanism that defers interrupt processing to schedulable tasks, preventing omissions in high-frequency scenarios. Evaluations confirm the method’s superiority: our SMP approach improved system lifespan by 25% through efficient load-balancing and maintained a 92% task completion rate despite core failures. It also handled high-frequency interrupts (below 1 kHz) with 100% completion and service latencies under 100 ms. Ultimately, our proposed RTOS significantly enhances robustness and reliability, making it a highly suitable solution for demanding automotive applications where system integrity is critical.
Volatile memory resident encrypted code
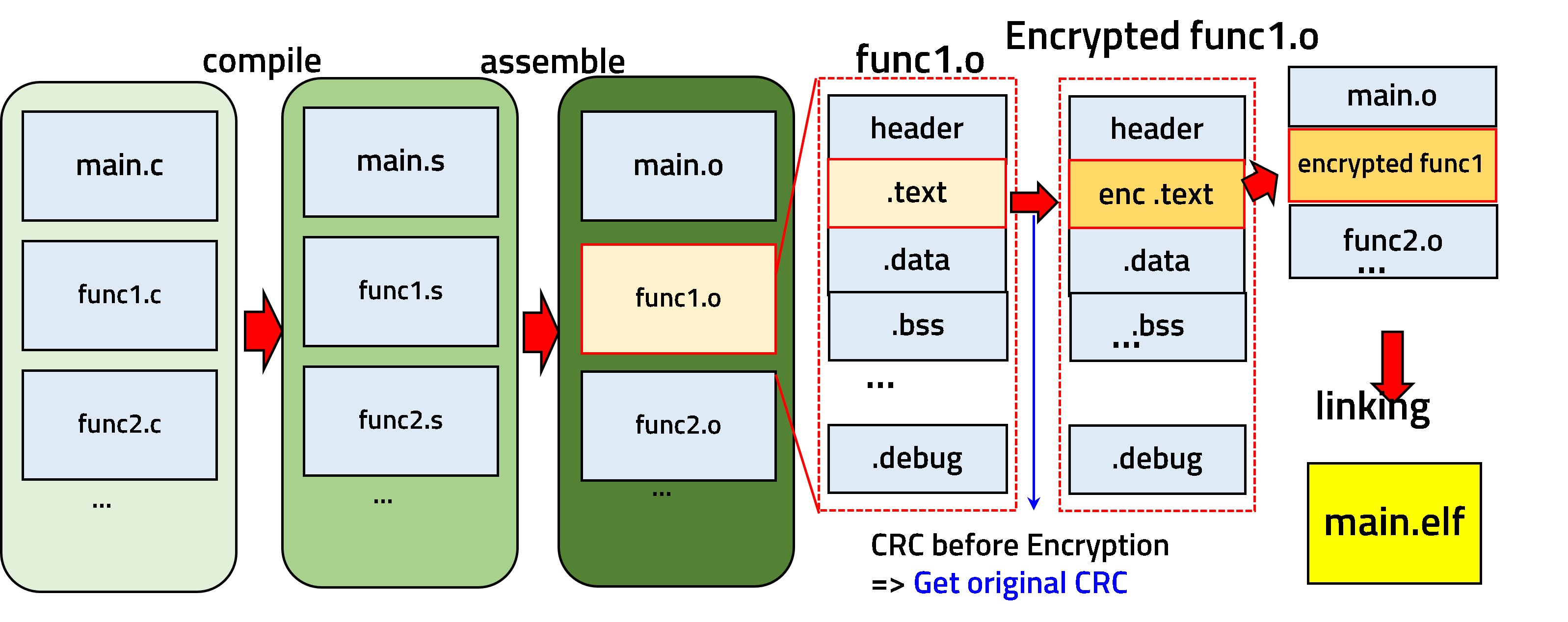 Executing code directly from non-volatile flash memory in microcontrollers (MCUs) presents security issues, as it is vulnerable to reverse engineering and bit-level manipulation attacks. These vulnerabilities can lead to sensitive information leaks, especially when physical access to the device is possible.
This work proposes a novel security enhancement method to address these problems by storing code in an encrypted format in flash memory and executing it from volatile memory (RAM) only when required. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and tampering by decrypting sensitive code immediately before runtime and verifying its integrity using CRC.
Furthermore, security is strengthened by dynamically allocating the decrypted code into RAM, which implements an Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) effect. This study shows that the proposed technique can effectively mitigate common security threats in applications like automotive electronics and IoT devices, presenting a robust solution for embedded system security.
Executing code directly from non-volatile flash memory in microcontrollers (MCUs) presents security issues, as it is vulnerable to reverse engineering and bit-level manipulation attacks. These vulnerabilities can lead to sensitive information leaks, especially when physical access to the device is possible.
This work proposes a novel security enhancement method to address these problems by storing code in an encrypted format in flash memory and executing it from volatile memory (RAM) only when required. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and tampering by decrypting sensitive code immediately before runtime and verifying its integrity using CRC.
Furthermore, security is strengthened by dynamically allocating the decrypted code into RAM, which implements an Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) effect. This study shows that the proposed technique can effectively mitigate common security threats in applications like automotive electronics and IoT devices, presenting a robust solution for embedded system security.
Publications
Journal Publication (SCI 3, KCI 3)
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Dynamic Round Robin Scheduling based Hypervisor System for Managing Multiple Operating Systems on Lightweight Microcontrollers (KCI) Journal of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, 2024.
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Filtering Time Optimization in Vehicle Electronic Control Systems Using a Non-Contact Magnetic Sensor and Dual Buffer Structure (KCI) IEMEK Journal of Embedded Systems and Applications, 2024.
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Ultralight Situation-Aware Hypervisor with Adaptive Starvation-Free Feedback Control for Embedded Systems (SCI) IEEE Access, 13:136643-136655, 2025.
Seungmin Lee, Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Non-Contact Magnetic Sensor-based Automotive Control Calibration for Low-Power Embedded Systems (SCI) IEEE Access, 2025
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. On Preparation (SCI) IEEE Transactions on Dependable Secure Computing, 2025.
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. On Preparation (KCI) IEMEK Journal of Embedded Systems and Applications, 2025.
Conference Publications (Intl. 5)
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Efficient Execution of On-Chip Embedded Software Using Pre-Emulation on Shallow OS In 14th International Conference on Mobile Computing and Ubiquitous Networking (Flagship Conf. ICMU 2023), 2023.
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Implementation of Dynamic Round Robin Scheduling on Bare-Metal Shallow Multi-OS for Lightweighted Microcontrollers In IEEE International Conference on Computers, Software, and Applications (Top Conf. COMPSAC 2024), 2024.
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Enhancing Microcontroller Security Through Volatile Memory-Resident Encrypted Code In IEEE Conference on Dependable Secure Computing (Top Conf. DSC 2024), 2024.
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Implementation of an SMP-based RTOS for Optimized Multicore Utilization on TriCore Architecture (Under Review) In IEEE International Technical Conference on CircuitsSystems, Computers and Communications (ITC-CSCC 2025), 2025.
Minjung Kim and Daejin Park. Efficient Load Balancing for On-chip Symmetric Multiprocessing through a Novel RTOS Approach for Multicore Microcontrollers In IEEE International Conference on Embedded MulticoreManycore Systems-on-Chip (Flagship Conf. MCSoC 2025), 2025.
Participation in International Conference
IEEE ICMU 2023, Kyoto, Japan
IEEE COMPSAC 2024, Osaka, Japan
IEEE EMSOFT 2024, Raleigh, USA
IEEE DSC 2024, Tokyo, Japan
IEEE ITC-CSCC 2025, Seoul, Japan
IEEE MCSoC 2025, Singapore, Singapore
Last Updated, 2025.12.12