Myeongjin Kang (Ph.D. 25, Ph.D. Agency for Defense Development (ADD) 국방과학연구소 박사급 선임연구원 )
 |
Ph.D Candidate. |
Repository Commit History
 |
Introduction
Full Bio Sketch
Mr. Kang received his B.S. degree in Electronics Engineering at Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea in 2020. He is currently a integrated Ph.D. student in School of Electronics Engineering at Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea. His research interests include the robust execution techniques of microcontroller. The techniques for robust execution includes processing of ECC and analysis of power consumption data in embedded systems. His research direction pursues performance improvement, low power consumption, and size reduction based on robust execution for the development of microcontrollers. Currently, he is conducting research on analyzing processor bus communication with mcahine learning for error detection and error prediction for robust execution.
Research Topic
ECC-Protected Robust Processors
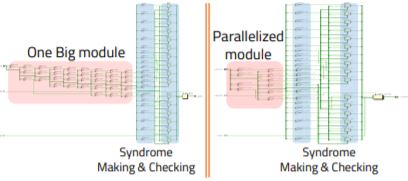 A tiny processing unit (TPU) activated with insufficient power always has a problem with data protection. To solve this problem, many TPUs and embedded systems use error-correcting code (ECC), especially Hamming code. However, adding an ECC decoding block to the TPU can cause a bottleneck. Most TPUs that follow a Von Neumann structure spend large amounts of time in the instruction fetch stage. The instruction fetch time increases due to ECC decoding intensifying the bottleneck. In this research, we propose an architecture for a parallelized ECC decoding block. Although it increases memory usage, the parallelized ECC decoding block speeds up the entire TPU by more quickly processing the ECC decoding. This architecture was synthesized and validated with Design Compiler and showed successful performance improvements using proposed architecture.
A tiny processing unit (TPU) activated with insufficient power always has a problem with data protection. To solve this problem, many TPUs and embedded systems use error-correcting code (ECC), especially Hamming code. However, adding an ECC decoding block to the TPU can cause a bottleneck. Most TPUs that follow a Von Neumann structure spend large amounts of time in the instruction fetch stage. The instruction fetch time increases due to ECC decoding intensifying the bottleneck. In this research, we propose an architecture for a parallelized ECC decoding block. Although it increases memory usage, the parallelized ECC decoding block speeds up the entire TPU by more quickly processing the ECC decoding. This architecture was synthesized and validated with Design Compiler and showed successful performance improvements using proposed architecture.
Safe Software Execution using Sensor-Fusion
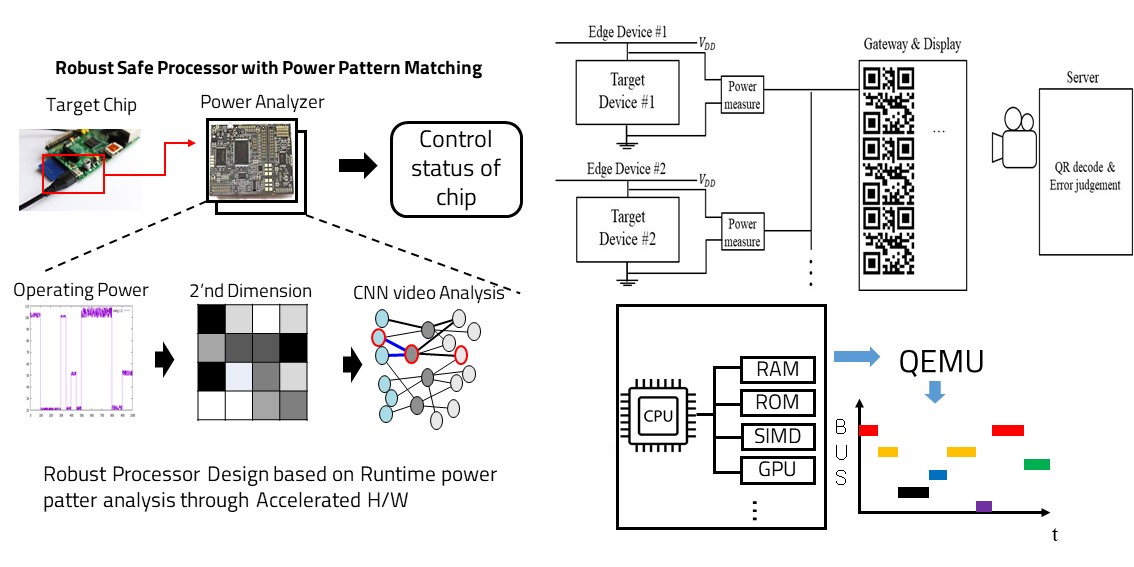 If an error occurs in a system where several edges are gathered and operated together, the error may be transferred to other edges or the entire system may be down. Therefore, it is important to judge and control the errors of each edge in such a system, which puts a load on the embedded system of small edges. To solve this problem, we show that the server can determine errors using the power consumption data, and the data consumption allows the server to read data values through data communication using QR codes. The proposed architecture was implemented using chip-whisperer to measure edges and data, as well as raspberry pi to implement the server. In the next, we plan to study additional error detection techniques by learning the bus analysis data of the processor through machine learning.
If an error occurs in a system where several edges are gathered and operated together, the error may be transferred to other edges or the entire system may be down. Therefore, it is important to judge and control the errors of each edge in such a system, which puts a load on the embedded system of small edges. To solve this problem, we show that the server can determine errors using the power consumption data, and the data consumption allows the server to read data values through data communication using QR codes. The proposed architecture was implemented using chip-whisperer to measure edges and data, as well as raspberry pi to implement the server. In the next, we plan to study additional error detection techniques by learning the bus analysis data of the processor through machine learning.
Cloud-Edge Connected Online Computing for Seamless Edge AI Serives
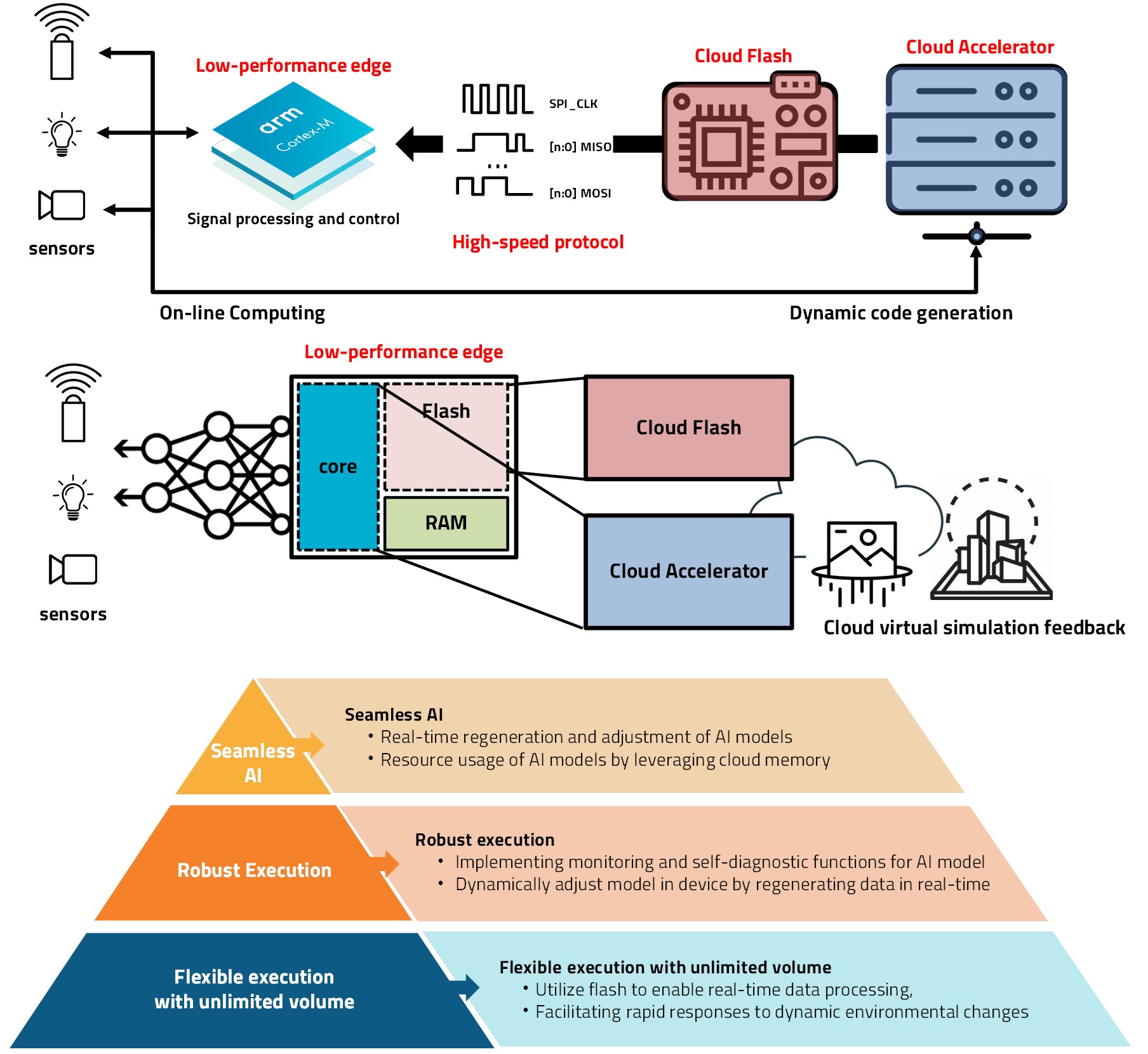 This research aims to empower low-performance edge devices with the ability to execute AI tasks seamlessly in real-time. Beyond using lightweight models for simple inference, study focuses on dynamic adaptation to new environmental conditions, enabling real-time sensor control and signal processing tailored to specific contexts. To achieve this objective, the research employs a novel approach. It involves reconstructing sensor data through virtual simulations hosted on a server, which serves as a cloud accelerator for the edge devices. Subsequently, code generation based on these simulations allows for the creation of adaptive algorithms. These algorithms are then transmitted to the edge devices via high-speed parallel communication channels, enabling them to execute AI tasks in real-time while seamlessly adjusting to changing environmental factors. This approach ensures that the edge devices can efficiently respond to dynamic situations, enhancing their overall performance and utility in various application domains. Through this research, several advantages can be obtained, including seamless AI operation, robust execution, and flexible execution with unlimited volume. These benefits enhance the reliability, adaptability, and scalability of AI execution in edge computing environments.
This research aims to empower low-performance edge devices with the ability to execute AI tasks seamlessly in real-time. Beyond using lightweight models for simple inference, study focuses on dynamic adaptation to new environmental conditions, enabling real-time sensor control and signal processing tailored to specific contexts. To achieve this objective, the research employs a novel approach. It involves reconstructing sensor data through virtual simulations hosted on a server, which serves as a cloud accelerator for the edge devices. Subsequently, code generation based on these simulations allows for the creation of adaptive algorithms. These algorithms are then transmitted to the edge devices via high-speed parallel communication channels, enabling them to execute AI tasks in real-time while seamlessly adjusting to changing environmental factors. This approach ensures that the edge devices can efficiently respond to dynamic situations, enhancing their overall performance and utility in various application domains. Through this research, several advantages can be obtained, including seamless AI operation, robust execution, and flexible execution with unlimited volume. These benefits enhance the reliability, adaptability, and scalability of AI execution in edge computing environments.
Event-Driven Edge AI Software Offloading Scheduling
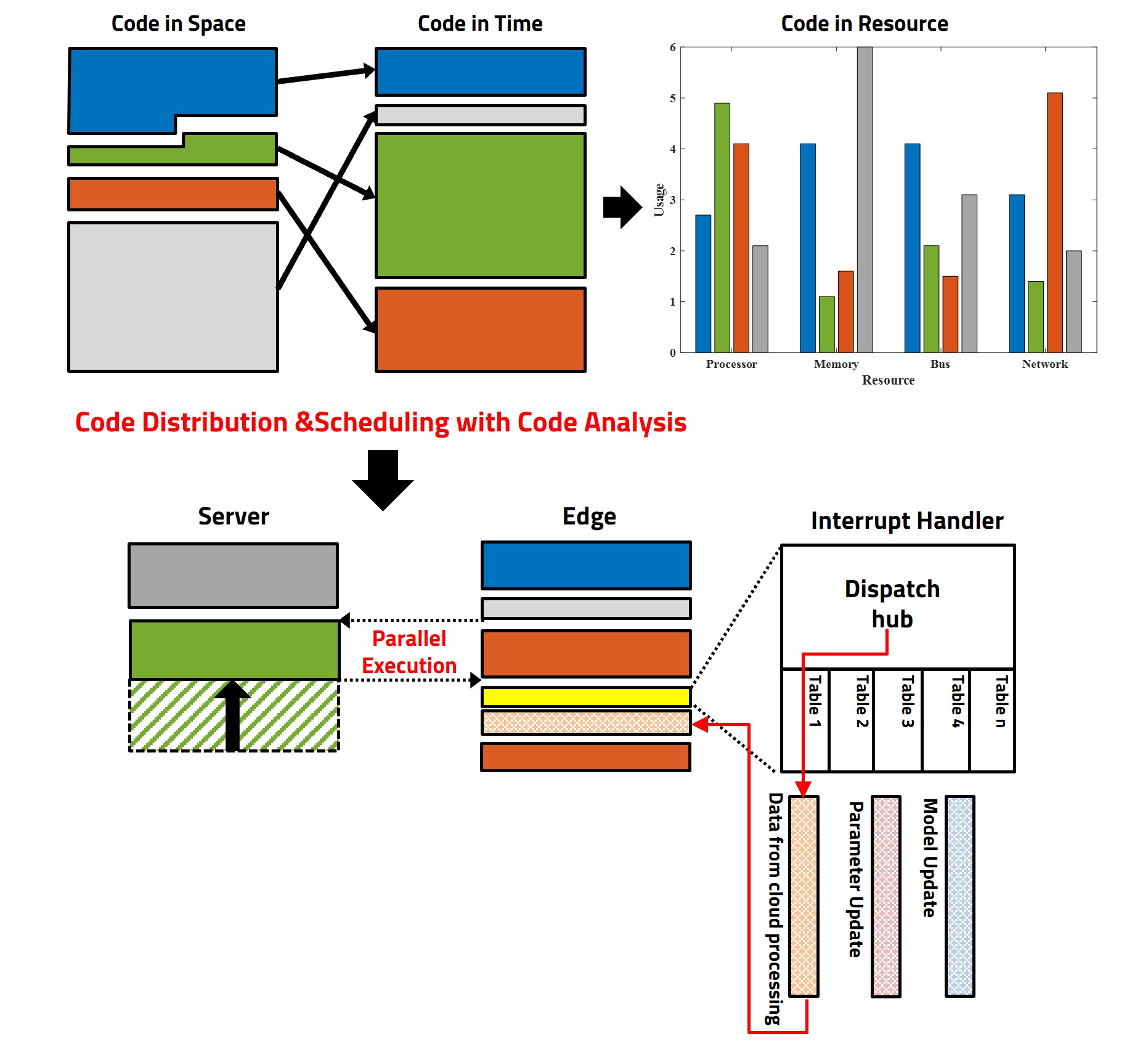 The trend of executing AI software using edge devices’ own hardware is increasing. However, for tasks requiring large-scale computations such as learning and preprocessing, data is often transmitted to a server for execution and the edge device waits for the response. While the server processes data much faster than the edge device, the uncertainty regarding processing time and required resources causes the edge device to remain in a polling state. Therefore, there is a need for interrupt and event-driven based scheduling of edge AI software. The research focus is on identifying dependencies through AI software analysis, scheduling AI software based on analysis of execution time relative to code and parameter data size, and developing interrupt and event-driven based edge-server parallel processing techniques. By analyzing AI software code in terms of dependencies, size, execution time, and resource usage, the code is restructured to operate in an event-driven manner based on interrupts rather than polling on the edge device. This enables complete parallel processing between the server and the edge, allowing the edge device to operate independently of server performance. Additionally, the interrupt-based approach allows for dynamic responses to server results.
The trend of executing AI software using edge devices’ own hardware is increasing. However, for tasks requiring large-scale computations such as learning and preprocessing, data is often transmitted to a server for execution and the edge device waits for the response. While the server processes data much faster than the edge device, the uncertainty regarding processing time and required resources causes the edge device to remain in a polling state. Therefore, there is a need for interrupt and event-driven based scheduling of edge AI software. The research focus is on identifying dependencies through AI software analysis, scheduling AI software based on analysis of execution time relative to code and parameter data size, and developing interrupt and event-driven based edge-server parallel processing techniques. By analyzing AI software code in terms of dependencies, size, execution time, and resource usage, the code is restructured to operate in an event-driven manner based on interrupts rather than polling on the edge device. This enables complete parallel processing between the server and the edge, allowing the edge device to operate independently of server performance. Additionally, the interrupt-based approach allows for dynamic responses to server results.
Cloud-generated Dynamic Code for Edge Streaming AI
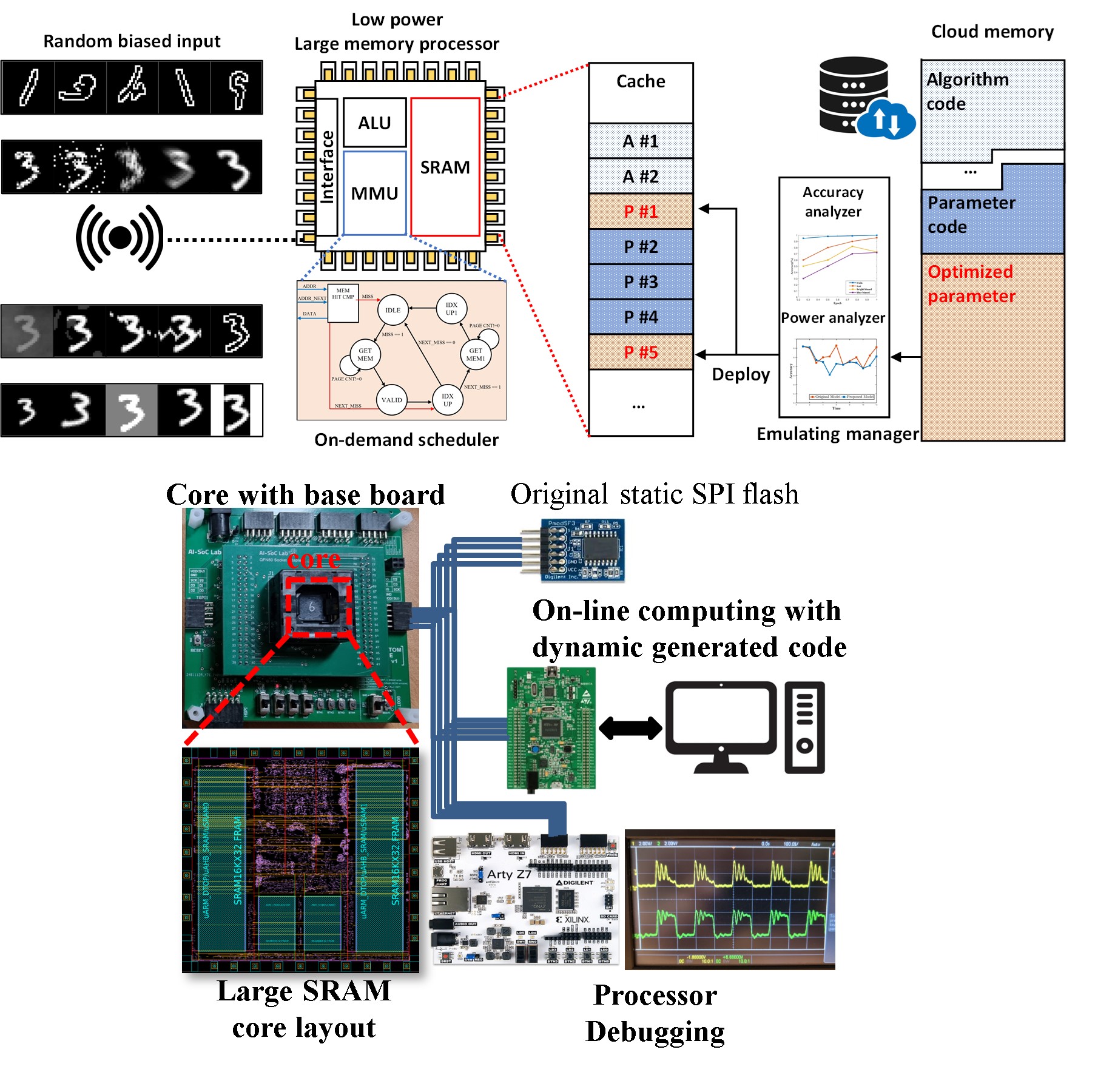 Edge devices typically rely on static on-chip flash memory, which makes it difficult to adapt AI software to changing environments. Dynamic code generation in the cloud allows AI modules to be delivered to the edge without storing the entire software locally. This reduces memory constraints and supports flexible execution. This work investigates a cloud-driven code streaming platform for edge devices. The study implements dynamic synthesis, compilation, and linking of AI modules in the cloud. The goal is to realize a runtime execution framework that supports adaptive AI software at the edge.
Edge devices typically rely on static on-chip flash memory, which makes it difficult to adapt AI software to changing environments. Dynamic code generation in the cloud allows AI modules to be delivered to the edge without storing the entire software locally. This reduces memory constraints and supports flexible execution. This work investigates a cloud-driven code streaming platform for edge devices. The study implements dynamic synthesis, compilation, and linking of AI modules in the cloud. The goal is to realize a runtime execution framework that supports adaptive AI software at the edge.
Cloud Emulator Monitoring System for Parameter Retraining
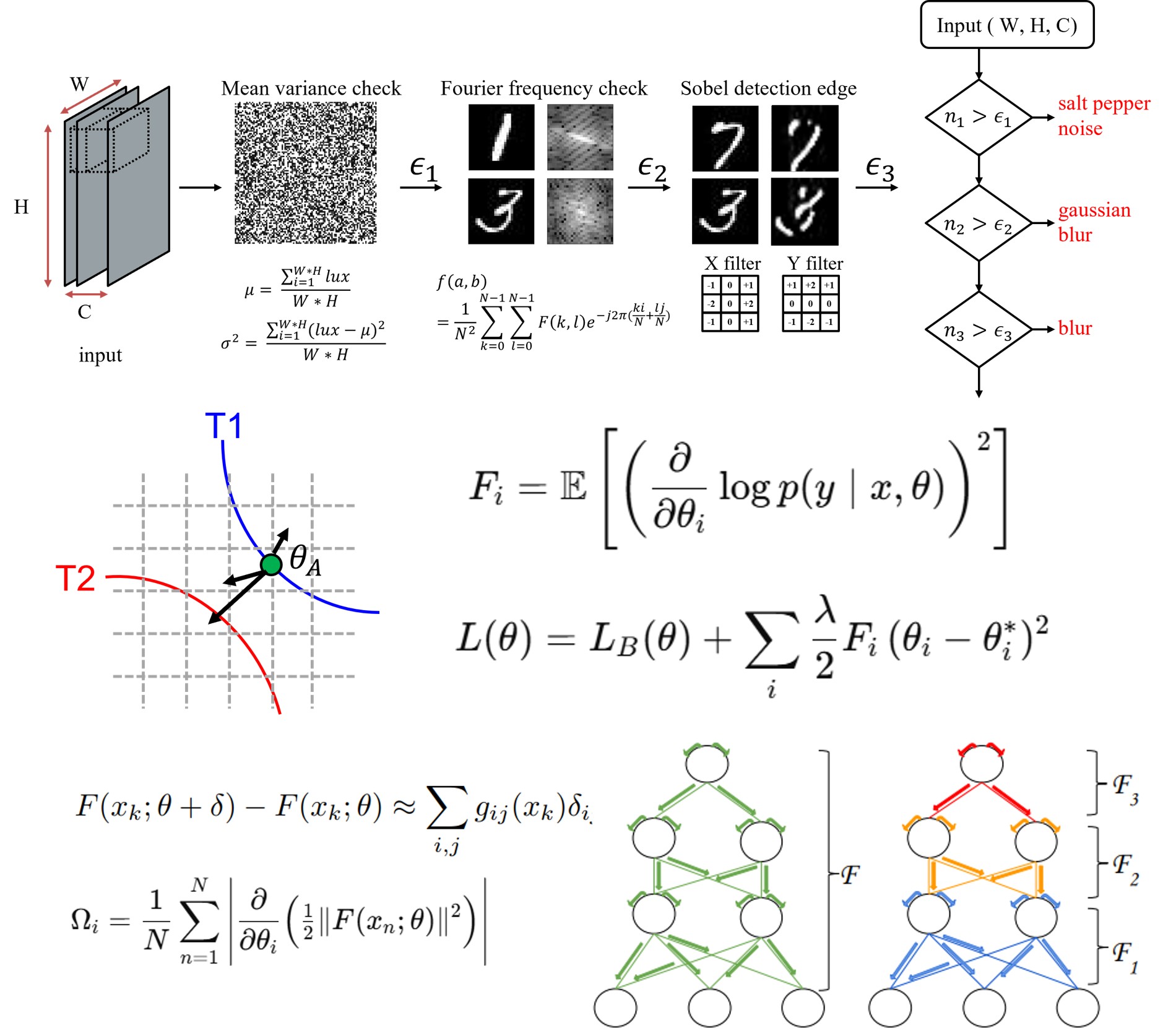 Inference accuracy at the edge often decreases when the input data contains noise or bias. A cloud emulator can observe inference behavior and determine which layers or parameters should be adjusted. Transmitting only selected parameters instead of the full model reduces update time and communication cost. This research proposes a cloud emulator monitoring system that tracks the status of edge inference. It focuses on selective parameter extraction and efficient update transmission. The aim is to improve inference robustness while maintaining low communication overhead.
Inference accuracy at the edge often decreases when the input data contains noise or bias. A cloud emulator can observe inference behavior and determine which layers or parameters should be adjusted. Transmitting only selected parameters instead of the full model reduces update time and communication cost. This research proposes a cloud emulator monitoring system that tracks the status of edge inference. It focuses on selective parameter extraction and efficient update transmission. The aim is to improve inference robustness while maintaining low communication overhead.
FPGA-Accelerated Incremental Relearning and Partial Update for Robust Edge Inference
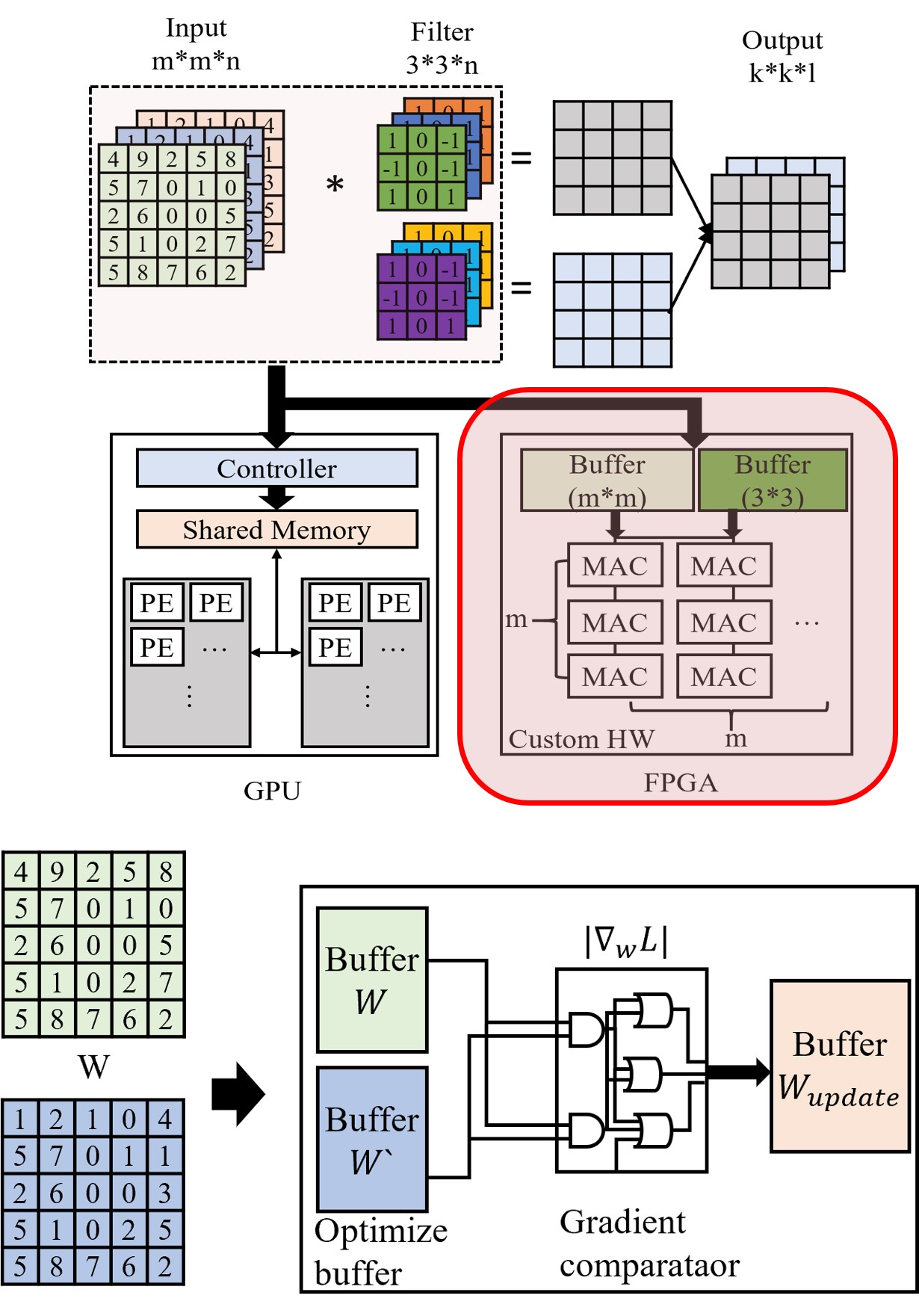 Incremental learning enables adaptation to new data without retraining the full model, but software-only approaches can be slow and resource-intensive. FPGA acceleration offers parallelism and hardware-level efficiency for incremental updates. This helps to meet real-time requirements in edge inference under changing conditions. The study develops FPGA-based acceleration techniques for incremental learning and partial updates. It explores hardware-software co-design methods to reduce retraining overhead. The focus is on achieving robust edge inference with faster adaptation using FPGA resources.
Incremental learning enables adaptation to new data without retraining the full model, but software-only approaches can be slow and resource-intensive. FPGA acceleration offers parallelism and hardware-level efficiency for incremental updates. This helps to meet real-time requirements in edge inference under changing conditions. The study develops FPGA-based acceleration techniques for incremental learning and partial updates. It explores hardware-software co-design methods to reduce retraining overhead. The focus is on achieving robust edge inference with faster adaptation using FPGA resources.
Publications
Journal Publications (KCI 5, SCI 4)
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. High Speed and Robust Processor based on Parallelized Error Correcting Code Module (KCI) Journal of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, 2020.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Lightweight Microcontroller with Parallelized ECC-based Code Memory Protection Unit for Robust Instruction Execution in Smart Sensors (SCI) Sensors, 2021.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Abnormal System Operation Detection by Comparing QR Code-Encoded Power Consumption Patterns in Software Execution Control Flow (KCI) Journal of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, 25(11):1581-1587, 2021.
Juneseo Jang, Myeongjin Kang, and Daejin Park. Low-Power On-Chip Implementation of Enhanced SVM Algorithm for Sensors Fusion-based Activity Classification in Lightweighted Edge Devices (SCI) Electronics, 11(1):139-159, 2022.
Myeongjin Kang, Ho Kim, Jungwon Park, Seongbum Yang, Junseo Yun, and Daejin Park. Low-Power Streamable AI Software Runtime Execution based on Collaborative Edge-Cloud Image Processing in Metaverse Applicaitons (KCI) Journal of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, 2022.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Digital Twin Technique for Effective Simulation of Interoperation with Users and Heterogenous Things (KCI) Journal of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, 27(4):503-510, 2023. Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Flexible Edge-AI Software Execution Architecture based on Cloud-Connected Incremental Learning (SCI) IEEE Access, 13:120772-120784, 2025.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Runtime-Robust Edge Inference System with Masking-Based Partial Update on Dynamic Reconfigurable FPGA (SCI) Sensors (SCI), 2025.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. On Preparation (KCI) (On Writing) Journal of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, 2025.
Conference Publications (Intl. 9)
Myungjin Kang and Daejin Park. Hue Based Effective Face Detection Using IoT Cooperation for Standby Power Reduction In The 5th International Conference on Next Generation Computing 2019 (ICNGC), 2019.
Myungjin Kang and Daejin Park. Robust On-Chip Processing Unit with Parallelized ECC Block for Lightweight Instruction Execution In 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics - Taiwan, 2020.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Remote Monitoring Systems of Unsafe Software Execution using QR Code-based Power Consumption Profile for IoT Edge Devices In IEEE ICEIC 2021, 2021.
Myeungjin Kang and Daejin Park. Robust Reconstruction of QR-Embedded Software using CRC-based Sequence Extraction of Asynchronous Time-Multiplexed QR Code In IEEE ICCE-Asia 2021, 2021.
Juneseo Jang, Myeongjin Kang, and Daejin Park. Accelerated SVM Algorithm for Sensors Fusion-Based Activity Classification in Lightweighted Edge Devices In IEEE 40th International Conference on Consumer Electronics, 2022.
Ho Kim, Jungwon Park, Seungbeom Yang, Junseo Yun, Myeognjin Kang, and Daejin Park. Edge-Cloud Cooperative Image Processing by Partially Streaming ROI Data for Metaverse Applications In IEEE ICCE-Asia 2022, 2022.
Myeongjin Kang, Nayoung Kwon, Seungmin Lee, and Daejin Park. Fast Bit Inversion Vulnerability Pre-estimation using Tcl and UPF in RTL Simulation Runtime In IEEE International Conference on ICT Convergence (ICTC 2023), 2023.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Cloud Memory Enabled Code Generation via Online Computing for Seamless Edge AI Operation In IEEE COMPSAC 2024, 2024.
Myeongjin Kang and Daejin Park. Runtime Noise Robust Edge Inference with Incremental Learning and Partial Update using FPGA Accelerator In IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics Asia (ICCE-Asia 2025), 2025.
Patents (Total 1 Patents Pending)
Edge Computing System and Edge Computing Method In Korea Patent and Tradmark Office, Dec 2024. Korea Patent Pending
Participation in International Conference
IEEE COOLChips 2019, Yokohama, Japan
IEEE GCCE 2019, Osaka, Japan
ICNGC 2019, Chiang Mai, Thailand
ICEIC 2020, Barcelona, Spain
IEEE ICCE-TW 2020, Taipei, Taiwan
IEEE ICEIC 2021, Jeju, Korea
IEEE ICCE-Asia 2021, Kangreong, Korea
IEEE ICCE 2022, Las Vegas, USA
ACM HPDC 2022, Minesota, USA
IEEE ICCE-Asia 2022, Yeosu, Korea
ACM Multimedia ASIA 2022, Tokyo, Japan
IEEE ICTC 2023, Jeju, Korea
IEEE COMPSAC 2024, Osaka, Japan
IEEE ICCE-Asia 2025, Busan, Korea
Last Updated, 2025.12.05